“Color coding” is used in electronics to identify between different components. In the case of resistors, color coding is used to identify a specific resistance value, for example a 100 ohms resistor or a 1 kilo ohms resistor with 5% tolerance. Electronic components like resistors are very small in size and its difficult to print its value directly on to the component surface. Hence a standard was formed in 1920 by then Radio Manufacturers Association (now part of EIA – Electronic Industries Alliance) to identify values and ratings of electronic components by printing color codes on them. Color coding technique makes it easy to print values (based on color codes) on small components, such as resistors and facilitates cost effective manufacturing.
This technique of “color coding” has 2 disadvantages. The first one appeals to general users where it becomes difficult to distinguish between colors (for example “Red” and “Brown” ) when the component is over heated. But this is not a major concern as the exact value can be easily identified using a multimeter (in case of confusion). The next drawback is for a specific group of people – color blind people can not identify the device using color codes. However they too can depend on multimeter to identify resistance values.
Latest Products
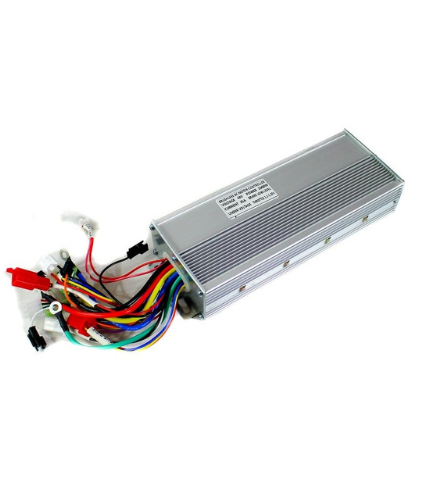
48V 1000W BM1109 EBIKE Brushless Controller
Highlights:
- This is a superpower brushless controller for BM1109
- Fit for 48v 1000w brushless motor
- Controller adaptors waterproof design
- Suitable for electric scooter, e-bike, tricycle, mini bike, pocket bike, go-kart, ATV, moped
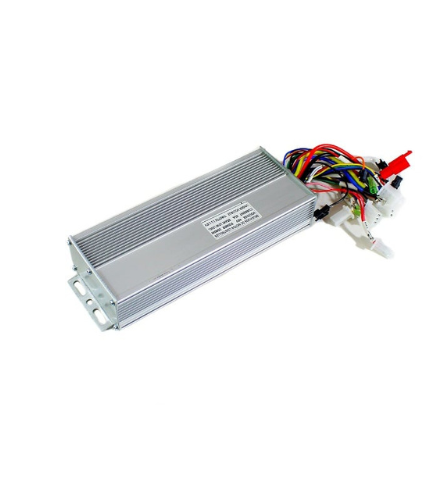
48V 1000W EBIKE Brushless Controller
Highlights:
- Rated Voltage:48 V
- Rated Current:35 A
- Temperature range:-25 to 40 degrees Celcius
- Weight:640 gm
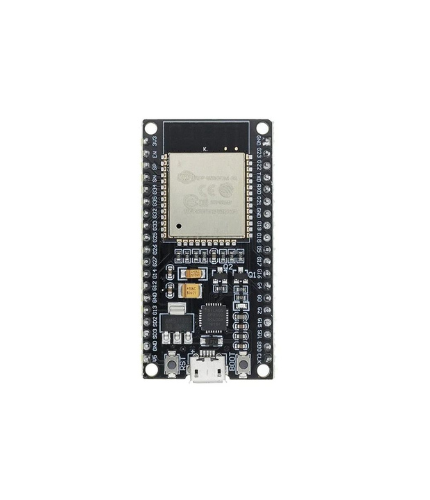
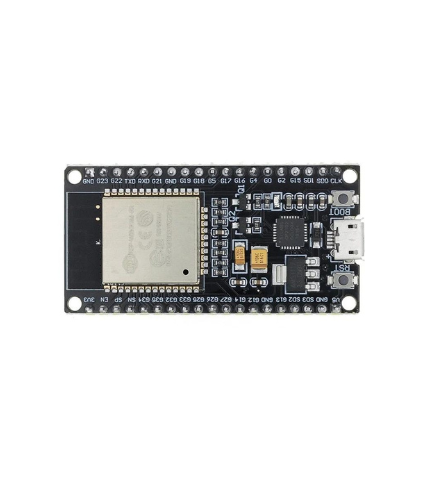
ESP32 38Pin Development Board WiFi+Bluetooth Ultra-Low Power Consumption Dual Core
Highlights:
1. 2.4GHz Dual-Mode WiFi + Bluetooth Development Board, 38PIN
2. Ultra-Low power consumption works perfectly with the IDE
3. Support LWIP protocol, Freertos
4. Support Three Modes: AP, STA, and AP+STA
5. ESP 32 is safe, reliable, and scalable to a variety of applications
F450 / Q450 Quadcopter Frame(PCB Version with Integrated PCB) + Plastic Landing Gear Combo Kit
Highlights:
- Made of advanced engineering material, super strong & smooth
- Easy to assemble and disassemble.
- The frame is tough and durable.
- The main glass fiber frame has good strength.
- The arm equips support ridges for better and faster forward flight.
- Features pre-threaded brass sleeves.
- Large mounting tabs for camera mounting.
- In-built power distribution board.
- Arm mounting holes: 3 mm.
How to Identify Resistor Color Code:
The figure below shows the layout of the bands, the multiplier and the tolerance value of a resistor. For a 6-band resistor, an additional temperature coefficient band is provided.
The gap between the multiplier and the tolerance specifies the left and right side of the resistor. So here are the key points;
4 band resistor – has 3 color bands on left side and one color band on right side. First two bands represent significant digits, the 3rd band represents multiplier and the fourth band on right side represents tolerance.
5 band resistor – has 4 color bands on left side and one color band on right side. Here the first 3 color bands represent significant digits, fourth one represent multiplier and the 5th one on right side represents tolerance.
6 band resistor – has 4 color bands on left side and 2 color bands on right side. Here the first 3 color bands represents significant digits, fourth one represents multiplier, 5th one represents tolerance and the 6th one represents temperature coefficient of the resistor.
In a 4-band resistor, the first two bands represent the first two digits of the resistor. The multiplier band indicates the value that is to be multiplied with the first two digits. The tolerance band after the multiplier band indicates the range of accuracy of the resistor. It is represented in units of percentage. In case of 5 band resistor, the decimal multiplier will be assigned to the fourth band and tolerance value will be assigned to the fifth band. Finally in case of a 6 band resistor, the last band (i.e 6th band) represents temperature coefficient. .The sixth temperature coefficient band increases the precision of the resistance value. Temperature coefficient tells us the behavior of resistor under different heating conditions (means the variation in resistance values under normal conditions and over heated conditions)It is defined in units of ppm/K.